双向掺铒光纤放大器(Bi-EDFA)是空域有源光纤腔衰荡传感系统的关键器件, 其增益特性和噪声特性直接影响传感系统的稳定性。设计了适用于空域有源光纤腔衰荡传感系统的低增益、低噪声的增益钳制Bi-EDFA, 并应用Optisystem仿真软件对其进行优化。仿真结果表明: 通过优化设计, 可获得增益系数、噪声系数分别为15.35 dB、3.52 dB, 且能保持增益钳制的Bi-EDFA。
空域有源光纤腔衰荡传感系统 双向掺铒光纤放大器 增益钳制 低增益 低噪声 space domain active fiber cavity ring-down sensing bidirectional erbium-doped fiber amplifier gain clamped low-gain low-noise
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Engineering Laboratory for Fiber Optic Sensing Technology, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
2 Key Laboratory of Fiber Optic Sensing Technology and Information Processing, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
3 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Toronto, Toronto M5S-3G4, Canada
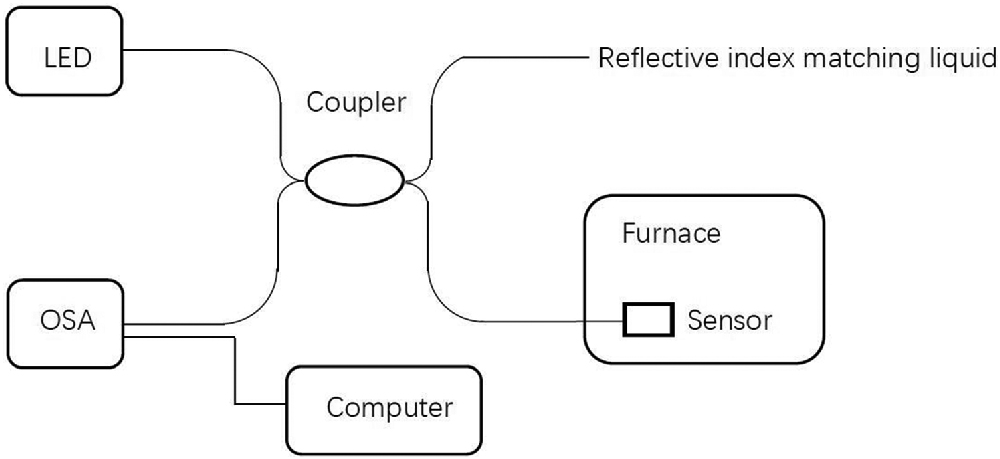
We propose a cavity length demodulation method that combines virtual reference interferometry (VRI) and minimum mean square error (MMSE) algorithm for fiber-optic Fabry–Perot (F-P) sensors. In contrast to the conventional demodulating method that uses fast Fourier transform (FFT) for cavity length estimation, our method employs the VRI technique to obtain a raw cavity length, which is further refined by the MMSE algorithm. As an experimental demonstration, a fiber-optic F-P sensor based on a sapphire wafer is fabricated for temperature sensing. The VRI-MMSE method is employed to interrogate cavity lengths of the sensor under different temperatures ranging from 28°C to 1000°C. It eliminates the “mode jumping” problem in the FFT-MMSE method and obtains a precision of 4.8 nm, corresponding to a temperature resolution of 2.0°C over a range of 1000°C. The experimental results reveal that the proposed method provides a promising, high precision alternative for demodulating fiber-optic F-P sensors.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.2300 Fiber measurements Chinese Optics Letters
2018, 16(1): 010606
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 National Engineering Laboratory for Fiber Optic Sensing Technology, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
2 School of Science, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
3 Key Laboratory of Fiber Optic Sensing Technology and Information Processing, Ministry of Education, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan 430070, China
We demonstrate a novel all-fiber cavity ring-down (CRD) magnetic field sensing method that uses frequency-shifted interferometry, and does not require any optical pulse and fast electronics compared with conventional CRD schemes. The sensing element in the ring-down cavity is a fiber taper surrounded by magnetic fluid, whose refractive index varies as an external magnetic field is applied. Magnetic field strength measurement is successfully achieved within a range from 8 to 850 Gs. A resolution of 0.00105 ± 0.00003 dB/Gs is obtained in the approximately linear segment from 423.2 to 766.6 Gs. The sensing method is potential for sensing other physical and chemical parameters.
060.2370 Fiber optics sensors 060.4370 Nonlinear optics, fibers 070.4340 Nonlinear optical signal processing 160.4670 Optical materials Chinese Optics Letters
2014, 12(12): 120604





